pGina MySQL Authentication Plugin Documentation
- Plugin Name: MySQL Authentication
- Plugin Type: Authentication, Gateway
- Version: 3.9.9.0
How it Works
The MySQL Authentication plugin authenticates users against account information stored in a MySQL database. The plugin connects to the MySQL server, retrieves the account information including password (possibly a hash), and compares the user supplied password with the one retrieved from the database. It registers success if the passwords (or hashes) match.
As of version 3.1, this plugin also supports adding users to local groups based on group membership information stored in the MySQL database.
The database schema is fairly flexible and configurable (see below).
Typical Setup
A typical (minimal) setup for MySQL Authentication is to enable the Local Machine plugin in the authentication and gateway stages, and enable MySQL Auth. in the authentication stage. Within the authentication stage, order the MySQL plugin before Local Machine.
The Database Schema
The schema includes three tables:
- A user table
- A group table
- A user-group table
The third table (user-group) links users to groups. It contains only two coumns. Each column is a foreign key linking to the user and group tables respectively.
The user table must have at least three or four columns (the column names can be configured):
- Username - The column containing the user name. This column should be unique (or the primary key).
- Hash Method - The hash method used for storing the password. This can be one of several strings (see below).
- Password - The (possibly hashed) password.
- Primary key - This column is the primary key for this table. This column can be the same as the username column.
If the primary key is the same as the username, then there are only three columns, otherwise there are four.
The Hash Method column can have one of the following values:
NONE- The password is stored in plain text.MD5,SHA1,SHA256,SHA384, orSHA512SMD5,SSHA1,SSHA256,SSHA384, orSSHA512(The salted versions of above)
The group table must have at least one or two columns (column names are configurable):
- Group name - The column containing the group name.
- Primary key - The primary key (can be the same as the group name column).
The user-group table must have exactly two columns which are foreign keys linking to the user and group tables:
- User foreign key - The foreign key to the user table.
- Group foreign key - The foreign key to the group table.
This table stores the group membership information.
Salted Passwords
If any of the salted hash methods are used, this plugin expects the data to be organized as follows. The password column must contain a hexadecimal or base 64 encoded string that contains the following:
encoding ( hash( password + salt ) + salt )
Where encoding converts to a string using either hexadecimal or base 64 encoding, and hash applies the appropriate hash algorithm.
Configuration
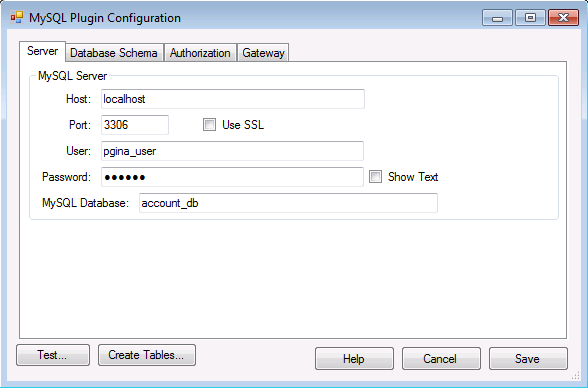
- Host – The IP or fully-qualified hostname of the MySQL server.
- Port – The port where the MySQL server process is listening.
- User – The username to use when connecting to the MySQL server.
- Password – The password to use when connecting to the MySQL server.
- Use SSL – Whether or not to use SSL encryption when connecting to the MySQL server. Note that for this to work correctly, your MySQL server must have SSL enabled. For more information on setting up a MySQL server with SSL, see the MySQL documentation.
- MySQL Database – The database containing the account information table.
Database Schema Configuration
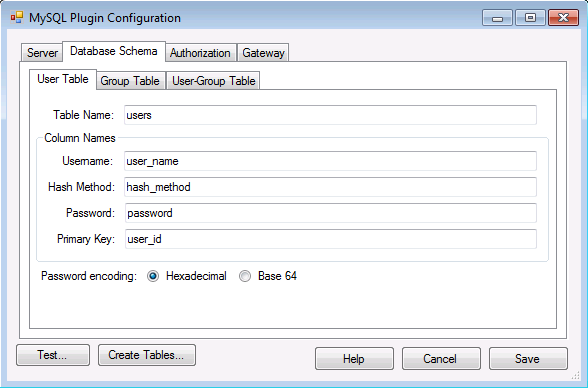
Under the “Database Schema” tab, you can configure the column names and table names. Note that any table may include more columns than those listed here. The primary key for the user table may have the same name as the username column. If so, they are treated as a single column. Similarly for the primary key for the group table.
The “Password encoding” radio buttons indicate the binary encoding used in the password column of the database.
The “Test…” button initiates a test of the MySQL connection, and verifies that the tables exist and are properly formatted.
The “Create Table…” button attempts to connect to the MySQL server and create the information tables.
Authentication Configuration
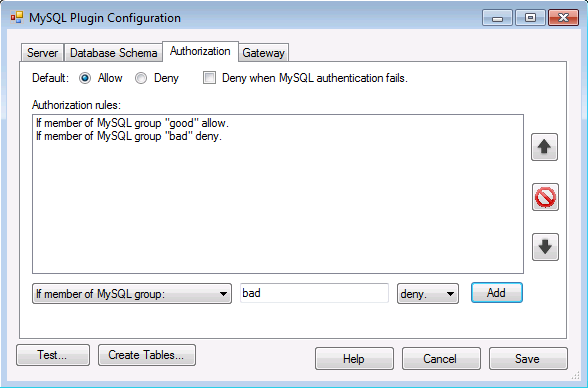
The authorization tab provides an interface for creating, removing, and deleting authorization rules. The rules are tested by the plugin in order and the first matching rule is applied. If none of the rules match, the default rule is applied. The default is configured using the radio buttons at the top of the tab interface.
- Default - If none of the rules match, the default rule is applied
- Deny when MySQL authentication fails - If this is checked, authorization fails when the MySQL plugin fails to authenticate the user in the authentication stage or the MySQL plugin does not execute in that stage.
Gateway Configuration
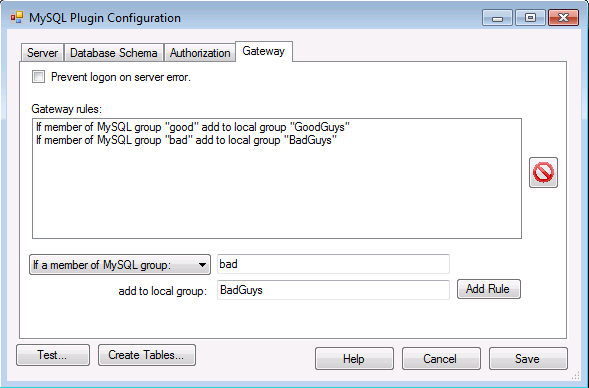
Under the “Gateway” tab you can configure a set of rules to be applied within the gateway stage. This allows you to add the user to local groups based on membership in MySQL groups.
